Let’s start with a simple question: Why should you care about the bore diameter and rod diameter when selecting a double rod cylinder for your application? Well, whether you’re running heavy machinery or automating an assembly line, the right cylinder dimensions aren’t just numbers. They determine thrust, stability, lifespan, and overall reliability of your pneumatic actuator.
Double rod cylinders are popular among B2B clients—especially those dealing with high-precision automation, robotics, and other equipment that require smooth, accurate bidirectional motion. Get this calculation wrong, and you might face frequent breakdowns, wasted energy, or even safety risks.
Walk you through how to determine the correct bore and rod size, peppering in tips, tables, and design recommendations that will help you choose the best CXSM Series Mini Cylinder double rod cylinder for your needs. If you’re unsure about your requirements, reach out—our engineers are happy to answer your inquiry or help with custom solutions!
Double Rod Cylinder Structure & Operating Principle
Before we jump into calculations, let’s look under the hood. What exactly is a double rod cylinder?
| Component | Description | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Bore | The internal diameter of the cylinder tube | Determines thrust and volume |
| Piston Rods | Two rods extending from both ends of the piston | Improve balance and control |
| Piston | Slides inside the cylinder tube; connects both rods | Transmits force |
| End Caps | Seal the ends; house mounting and rod passageways | Contain air/hydraulic pressure |
| Seals | Minimize leakage and prevent contamination | Ensure efficient operation |
The double rod cylinder is, in essence, a balanced actuator with a rod protruding from each side. When air enters either side of the piston, it moves in the chosen direction—providing equal thrust and stroke in both directions. This symmetry means higher stability, less chance of tilting, and more precise positioning for tasks like pick-and-place operations.
Pro Tip: If your system requires tools or sensors on both ends, or frequently reverses direction, the double rod design is your ideal match. Just ask our technical team for details or a quote.
Double Rod Cylinder Key Parameters for Sizing
It’s not just about the bore and the rod. Here’s a checklist of main parameters to consider before diving into formulas:
- Stroke Length — How far must the rod travel?
- Mounting Type — Will you use flange, foot, or rear trunnion?
- Load Weight — What’s the maximum force needed?
- Operating Pressure — Most cylinders run at 0.15 to 0.7 MPa (see table below).
- Space Constraints — Will the cylinder fit in your equipment?
- Speed Requirements — Do you need smooth, rapid motion or controlled movement?
- Cycle Frequency — How often does it actuate per day?
| Parameter | Typical Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke Length | 10–1000 mm | Longer stroke = larger bore needed |
| Operating Pressure | 0.15–0.7 MPa | Check with your air source |
| Load Weight | Varies by application | Heavier load = larger bore/rod |
Consider these variables before calculating dimensions. They keep your selection practical and safe.
Calculating Bore Diameter: The Power Behind the Motion
Ready to do some math? The bore diameter (D) directly determines the cylinder’s output force. Here’s the key formula:
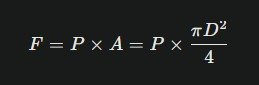
Where:
- FF: Required thrust force (N)
- PP: Operative pressure (Pa)
- DD: Bore diameter (mm)
For practical purposes, let’s put this into a simple step-by-step checklist:
1. Decide your required force (F)—based on load weight, friction, acceleration, and safety margins.
2. Confirm your available supply pressure (P).
3. Rearrange the formula to solve for D:
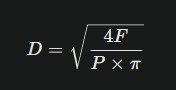
| Required Force (N) | Supply Pressure (MPa) | Bore Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 250 | 0.5 | 25.2 |
| 800 | 0.6 | 41.2 |
| 1800 | 0.7 | 57.2 |
| 3500 | 0.7 | 80.0 |
Always round up to the next standard bore size. For heavy-duty loads or high-speed motion, a larger bore offers more safety and room for future upgrades.
Want a real-life example for your industry or load? Click to request a personalized selection or get a free sizing worksheet.
Discover how Double Rod Cylinder boost your machine’s precision and durability. Contact us today for expert guidance and tailored solutions!
Double Rod Cylinder Calculating Rod Diameter: Strength, Stability, and Safety
The piston rod’s job is to withstand the force generated by the cylinder, without bending or snapping. If the rod is too thin, it could buckle under pressure, damaging both your actuator and your production schedule. Thankfully, there’s a simple way to estimate the minimum safe rod diameter.
Core Formula and Speed Ratio Considerations
For most double rod cylinders, designers recommend a speed ratio (rod diameter to bore diameter) between 0.3 and 0.4. But for higher load or extended strokes, go up to 0.5 for extra stiffness.
| Bore Diameter (mm) | Recommended Rod Dia (mm) | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 8 | 0.4 |
| 32 | 12 | 0.375 |
| 50 | 20 | 0.40 |
| 80 | 32 | 0.40 |
| 100 | 40 | 0.40 |
For rough calculation: d=k×D
Where:
- dd: Rod diameter (mm)
- DD: Bore diameter (mm)
- kk: Ratio (usually 0.35–0.4)
Dive deeper – Assessing rod rigidity isn’t just about formulas. Review your application for side loads, rapid acceleration, and mounting methods. For example, in vertical pick-and-place robots, go 10–20% higher on your rod diameter for high-speed cycles. For extra-long strokes, watch for buckling risk and consult with your manufacturer.
Have doubts about side loads, or high-cycle operation? Send us your project requirements for fast, expert advice and a quote on optimal rod sizing.
Advanced Sizing: Additional Detailed Considerations
Okay, quick question: Have you ever had a cylinder wear out too fast, or run unstable under repeated motion? Beyond just bore and rod calculations, these often result from other overlooked factors in your design:
- Mounting configuration: Flange, foot, or trunnion mounts affect allowable misalignment and rod buckling.
- Stroke length vs. rod diameter: As the stroke increases, rod flex and risk of bending rise. Add support guides for long strokes.
- Operating environment: High temperature, humidity, or corrosive conditions? Select compatible materials (stainless steel, specialty seals).
- End-of-stroke cushioning: Protects components against hard stops or impact.
Table: Matching Bore & Rod to Application Needs
| Application | Typical Bore (mm) | Typical Rod (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pick-and-place (robotics) | 20–32 | 8–12 | Fast motion, moderate load |
| Industrial conveyor | 40–63 | 16–25 | Longer stroke, heavier loads |
| Packing machinery | 32–50 | 12–16 | Frequent cycling, moderate stroke |
| Heavy assembly | 63–80 | 25–32 | High load, robust strength required |
| Custom automation | Any (ask us!) | Any (ask us!) | We’ll help you choose |
Remember: For special working conditions—think food-grade, chemical exposure, or outdoor use—our support team offers customization to extend cylinder life and protect against harsh elements. Just ask for a quick consultation or free sample.
B2B Industrial Application Examples
Let’s get real. Here are examples of how businesses actually select and use double rod cylinders in the field.
Example 1: Automated Assembly Line (Electronics)
A plant needs to move delicate components between two locations, at high speed but with low force.
| Load to Move | 40 N |
|---|---|
| Supply Pressure | 0.5 MPa |
| Stroke | 150 mm |
| Suggested Bore | D=0.5×106×π4×40 ≈ 10 mm |
| Suggested Rod | 4 mm (use ratio 0.4) |
Small, precise, rapid movement: choose a compact, high-speed cylinder. If unsure, send us a sketch—we’ll confirm the specs!
Example 2: Heavy Packaging Equipment
Conveyor must lift packs up to 200 kg at a moderate speed, with relentless daily operation.
| Load to Move | 1960 N (200kg × 9.8m/s²) |
|---|---|
| Supply Pressure | 0.6 MPa |
| Stroke | 500 mm |
| Suggested Bore | 65 mm |
| Suggested Rod | 26 mm (use ratio 0.4) |
For big jobs, always round up your bore and rod size—plus consider guide rod supports for ultra-long strokes. Shoot us a message for a professional check on fit and durability!
Selecting the correct bore and rod diameter for your double rod cylinder isn’t complicated, but it’s vital. Choose wisely, and you’ll enjoy stable, durable, and precise performance. Ignore the calculations, and you may end up with wasted time, unnecessary repairs, or unhappy customers.
Remember to factor in your load, pressure, stroke, and application needs. Browse our tables, use our formulas, and don’t hesitate to reach out to our engineers for advice or a custom quotation. With the right double rod cylinder, you’ll keep your automation humming—today and as your business grows.
FAQ
What rod diameter guarantees no bending or failure?
Stick to 0.35–0.4 times the bore diameter; go higher for high loads or long strokes.
Can I custom order a double rod cylinder for specialized equipment?
Yes, most manufacturers offer custom bores, rods, and mounts—send us your specs for fast quoting.
What are common bore and rod diameters on the market?
Standard bores: 20, 32, 50, 63, 80, 100 mm; paired with rods from 8–40 mm.
Are double rod cylinders better for automation than single rod?
Yes—balanced positional accuracy, less wear, and easier mounting for end-of-arm tools.