A compact air cylinder differs from a mini air cylinder mainly in terms of their dimensional structure, load capacities, and best-fit applications, even though both are designed to solve space constraints in modern automation. Compact cylinders are best when you need robust force in a short space, while mini cylinders are ideal for ultra-light-duty, micro-movement uses where installation space is extremely limited and speed or positioning may be more critical than power.
When every millimeter counts, finding the right pneumatic actuator can make or break an automation project. Many procurement specialists and technicians face a key decision: “Should I opt for a compact air cylinder or a mini air cylinder?” While both types are designed to operate in tight spots and boost the efficiency of machines, the differences between them can impact cost, performance, and installation.
What is a Compact Air Cylinder?
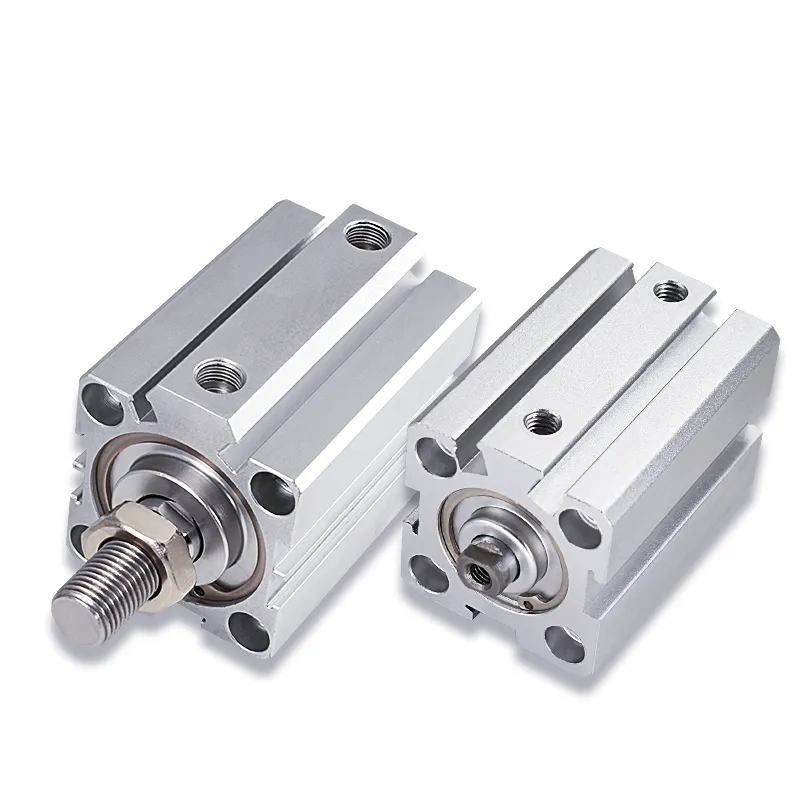
Compact air cylinders are space-saving pneumatic actuators engineered to deliver powerful linear force in a short-stroke, minimal-profile package. Despite being shorter than standard models, compact cylinders retain larger bore sizes, delivering the same force as their non-compact counterparts. That’s a game-changer for anyone retrofitting existing equipment or building new automated lines with limited installation depth. These devices are heavily used in electronics assembly, packaging machines, textile lines, and anywhere that speed, force, and reliability are priorities in a small footprint.
Key traits of compact air cylinders:
- Larger diameter bores in a shorter, square or round body
- High to medium force output for the size
- Commonly available with magnetic position sensors
- Short stroke (typically 5–50 mm)
- Easy to install on plates, end faces, or tight machine interiors
What is a Mini Air Cylinder?
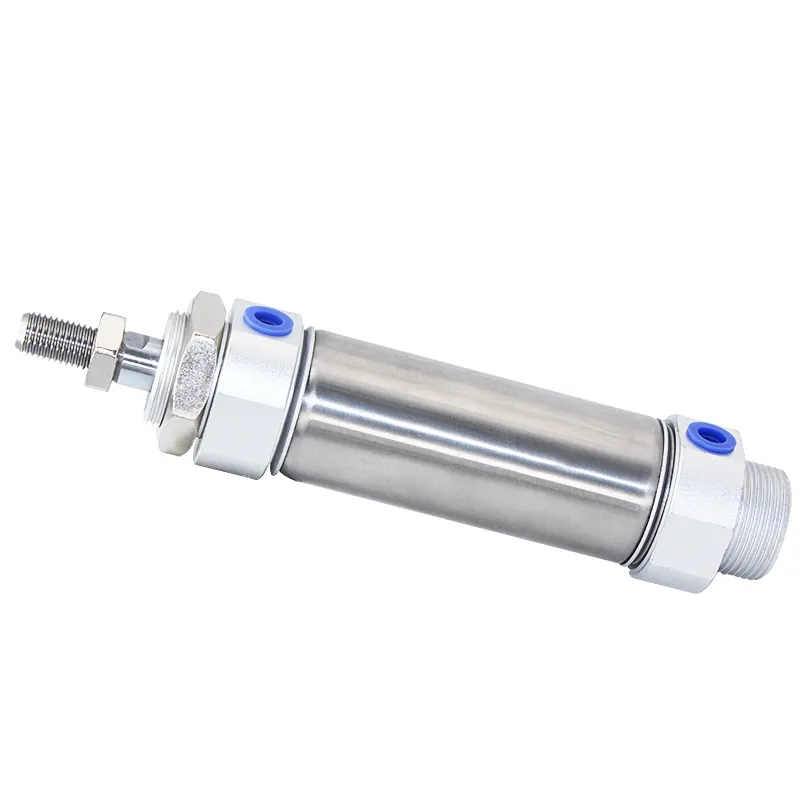
Mini air cylinders—sometimes called micro or miniature air cylinders—are tailored for very light-duty tasks where space, air consumption, and delicate movement are top priorities. They are typically round-bodied, with extremely small bore diameters (as small as 6 mm) and feature very lightweight builds. You’ll spot them in medical equipment, laboratory automation, pick-and-place robotics, or anywhere gentle, precise actuation is needed and system weight must be kept to a minimum.
Core features of mini air cylinders:
- Ultra-slim, lightweight construction, usually round and ISO 6432 compliant
- Small bore diameters (6 mm—25 mm typically)
- Designed for low load/low force applications
- Consume little compressed air—energy efficient for large networks
- Perfect for moving small parts or delicate positioning tasks
Differences Between Compact and Mini Air Cylinders
Let’s break down their main differences in an easy-to-read table, so you can compare side by side:
Selecting the Right Cylinder for Your Application
Choosing between these cylinders depends on a few critical questions:
What is your load requirement? If you need a strong push in a tight spot (think packaging or pressing), a compact air cylinder is the answer. For gentle, precision movement of tiny components, go with a mini air cylinder.
How much installation space is available? Mini cylinders win if you’re working with tiny or narrow machine slots, while compact cylinders fit where the stroke is short but bore (and thus force) must be higher.
Do you need special features? Need built-in feedback? Many compact cylinders support magnetic switches for smart, automated feedback, which is handy if you’re adding them to an IoT-enabled factory.
Popular Applications and Use Cases
Both types have broad usefulness, but favor different environments and roles:
Compact air cylinders power up automation tasks—think pick-and-place systems, automated doors, and high-speed industrial assembly lines where their punch and reliability are valued.
Mini air cylinders are perfect for tight spaces in labs, portable equipment, and light-positioning mechanisms, where machines must stay nimble and light.
Expert Tips for Maintenance and Installation
To get the most out of your pneumatic actuator, remember:
- Choose materials suitable for your environment—stainless steel or anodized aluminum for moisture, food, or high-corrosion areas.
- Always match cylinder bore and stroke with actual force needs to avoid wasting air or suffering poor motion quality.
- For compact cylinders, check that mounting holes or faces align perfectly with your assembly, as adjustment flexibility may be limited by their shape.
- Minis are easier to install and replace due to their simple round design—perfect for modular or quick-change setups.
The choice between a compact air cylinder and a mini air cylinder comes down to what matters most for your operation: force or finesse, power or precision. Understanding their differences not only maximizes your machine’s performance but also helps optimize your investment.
Ready to enhance your automation setup or need tailored recommendations for your project? Contact us for a fast quote or expert guidance—let’s make your pneumatic solutions smarter and more efficient today!
FAQ
Can compact and mini air cylinders be used interchangeably?
Do both types support position sensors?
Which type lasts longer?
How do I size my air cylinder?
Always size based on the required force, available pneumatic pressure, stroke length, and space. Many manufacturers provide guides or calculators to streamline this choice.
Can these cylinders handle side-loads or off-center forces?
Both types generally require precise alignment. If your application involves side-loads, consider models with integrated guides or multi-rod options for extra stability.