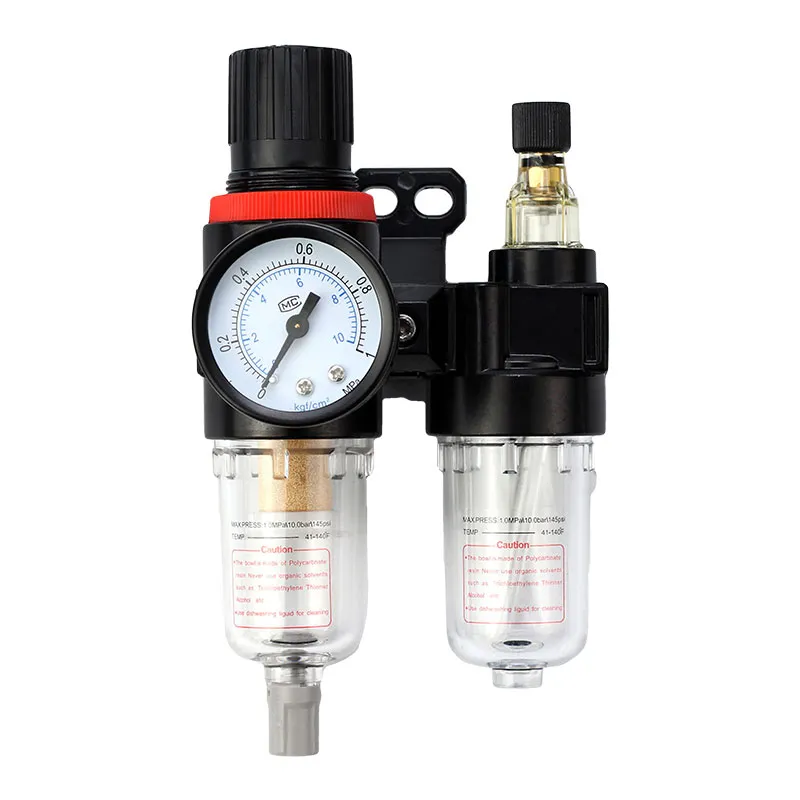
Introduction to air pressure reducing valve
The basic principle involves the regulating mechanism inside the valve:
1. Spring force balance system: The valve has a built-in spring force balance system, which is composed of springs and adjusting components. The spring provides restoring force to offset the gas pressure and keep the valve in a balanced state.
2. Adjusting element: The valve is equipped with an adjusting element, usually a rotatable screw or handle. By adjusting this component, the operator can change the size of the valve passage and thereby adjust the flow of gas through the valve.
3. Output pressure control: When the gas pressure in the system exceeds the set output pressure, the spring force is not enough to maintain balance, and the valve begins to open, allowing a portion of the gas to flow out until the output pressure returns to the set value. Vice versa, ensuring a constant pressure of the output gas.
4. Stability and accuracy: The spring force balance system gives the air pressure reducing valve stability and accuracy. Under different working conditions, the valve can be adjusted quickly and accurately to ensure a constant pressure of the output gas to meet system requirements.
Function: Due to its stability and adjustability, air pressure reducing valves are widely used in pneumatic systems, industrial automation and other occasions where accurate control of gas pressure is required. By properly adjusting the valves, you can ensure that pneumatic equipment operates normally under different pressures and improve the reliability and efficiency of the system.
A typical air pressure reducing valve consists of the following components:
1.Valve body: It is the main body of the air pressure reducing valve, made of metal or plastic. The function of the valve body is to accommodate the various components of the air pressure reducing valve and to act as a seal and support.
2.Valve seat: It is the seal of the air pressure reducing valve and is used to seal the flow of gas. Valve seats are usually made of metal or plastic.
3.Adjusting spring: Provides balancing force to help maintain the set output pressure. It is the elastic component of the air pressure reducing valve and is used to control the opening and closing of the valve core. Springs are usually made of steel or alloy.
4.Adjustment screw: used to manually adjust the output pressure.
Diaphragm: Isolates the valve seat and adjustment spring to prevent gas leakage.
working principle:
1.Primary valve seat adjustment: When gas passes through the valve, the primary valve seat controls the space through which the gas flows by adjusting the size of the channel, thereby achieving a preliminary pressure reduction.
2.Adjustment spring function: The adjustment spring is opposite to the output pressure. As the output pressure increases, the spring force becomes larger and the valve opens, allowing more gas to pass through. Vice versa, when the output pressure decreases, the spring force decreases and the valve closes, reducing the gas flow. The strength of the spring directly affects the output pressure of the air pressure reducing valve.
3.Adjustment Screw Manual Adjustment: By rotating the adjustment screw, the operator can manually adjust the output pressure to meet specific needs.
Classification and characteristics of air pressure reducing valves
Air pressure reducing valves can be divided into different types such as direct-acting type and indirect type according to their different structures and working principles.
1. Direct-acting air pressure reducing valve
Direct-acting air pressure reducing valves are a common type and their features include:
- Simple structure: The gas flow is adjusted directly through the valve core. The structure is relatively simple and the maintenance cost is low.
- Fast response speed: It can respond quickly to pressure changes and is suitable for occasions with high pressure regulation requirements.
2. Indirect air pressure reducing valve
The indirect air pressure reducing valve uses an indirect pressure regulating mechanism and has the following characteristics:
- Precise control: The valve core is indirectly controlled through the auxiliary device to achieve precise control of the output pressure.
- Strong adaptability: able to better adapt to changes in gas pressure under different working conditions.
Technical characteristics and performance indicators
1. Flow range: widely applicable. Ensure sufficient flow range under different working conditions to meet the needs of different applications.
2. Accuracy: High-precision adjustment. It has high-precision output pressure regulation and is suitable for systems with strict pressure control requirements.
3. Pressure resistance: strong stability. It can maintain stable operation under different pressure conditions to ensure system reliability.
Installation and maintenance of air pressure reducing valve
Install
1. Choose a suitable location:
When installing, be sure to choose a suitable location to ensure smooth air flow. Avoid selecting areas where blockage or foreign matter is present, which may affect the normal operation of the valve.
2. Adjust the primary valve seat:
During installation, the primary valve seat needs to be adjusted based on the gas pressure range of the specific application. This step is critical because it directly affects the initial pressure reducing effect of the valve. Make sure the primary valve seat is adjusted to the proper position to accommodate the operating requirements of the system.
maintain
1. Regular inspection:
Regular inspections are a critical step in ensuring proper operation of your air pressure reducing valve. During the inspection process, you need to pay attention to the following aspects:
- Leak check: Check all parts of the valve for leaks, especially the connection between the valve seat and the adjusting screw.
- Damage inspection: Check the valve for signs of damage or wear and make sure all parts are intact.
2. Cleaning and Lubrication:
Regular cleaning and lubrication are necessary steps to maintain the normal operation of the air pressure reducing valve:
- Cleaning: Clean dust and debris inside and outside the valve to keep the passage clear.
- Lubrication: Lubricate the moving parts of the valve to ensure flexibility and stability.
Application scenarios of air pressure reducing valve
1. In the field of mechanical processing, air pressure reducing valves are used to protect pneumatic tools, pneumatic machine tools and other equipment from being damaged due to excessive air source pressure.
- Pneumatic tools: In pneumatic tools, the air pressure reducing valve can prevent the pneumatic tool from being damaged due to excessive air source pressure. For example, in a pneumatic wrench, an air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to 6-8 bar, thereby protecting the cylinder and other parts of the pneumatic wrench from damage.
- Pneumatic machine tools: In pneumatic machine tools, the air pressure reducing valve can prevent the pneumatic machine tool from being damaged due to excessive air source pressure. For example, in a pneumatic punch press, the air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to 5-7 bar, thereby protecting the punch head and other parts of the machine tool from damage.
2. In the field of automation control, air pressure reducing valves are used to control pneumatic actuators, pneumatic valves and other equipment to meet the operating requirements of the system.
- Pneumatic actuator: Pneumatic actuator is an important component in the pneumatic system, used to convert air pressure signals into mechanical motion. The air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to the level required by the pneumatic actuator, thereby improving the operating efficiency of the pneumatic actuator. For example, in a pneumatic cylinder, an air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to 3-5 bar, thereby controlling the speed and stroke of the pneumatic cylinder.
- Pneumatic valve: Pneumatic valve is used to control the flow direction and flow rate of air flow. The air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to the level required by the pneumatic valve, thereby improving the control accuracy of the pneumatic valve. For example, in pneumatic stop valves, the air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to 2-4 bar, thereby ensuring that the pneumatic stop valve can reliably shut off the air flow.
3. In the food and pharmaceutical fields, air pressure reducing valves are used to control pneumatic conveying systems, pneumatic flushing systems, etc., to meet food safety and hygiene requirements.
- Pneumatic conveying system: Pneumatic conveying system is used to transport materials to designated locations. The air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to the level required by the pneumatic conveying system to prevent materials from being contaminated. For example, in pneumatic conveyors, air pressure reducing valves can reduce the air source pressure to 0.5-1 bar, thereby ensuring that materials are not contaminated during transportation.
- Pneumatic flushing system: Pneumatic flushing system is used to clean equipment or utensils. An air pressure reducing valve reduces the air source pressure to the level required for a pneumatic flushing system, thereby preventing equipment or appliances from being damaged. For example, in a pneumatic spray gun, the air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to 0.3-0.5 bar, thereby ensuring that the pneumatic spray gun can reliably spray cleaning fluid.
4. In the medical field, air pressure reducing valves are used to control pneumatic medical equipment to meet medical safety requirements.
- Pneumatic Medical Devices: Pneumatic medical devices are used for medical diagnosis and treatment. Air pressure reducing valves can reduce the air source pressure to the level required by pneumatic medical devices, thereby ensuring the safety and reliability of medical devices. For example, in a pneumatic anesthesia machine, an air pressure reducing valve can reduce the air source pressure to 0.2-0.3 bar, thereby ensuring that the anesthetic gas can be delivered evenly into the patient’s body.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What should I do if the air pressure reducing valve leaks?
A: Leakage may be caused by worn seals, loose valve seats, or damaged valves. Solutions include:
- Check the seals: Check the seals regularly for wear or aging and replace them if necessary.
- Tighten the valve seat: If the valve seat is found to be loose, tighten the valve seat in time.
- Replace damaged parts: If the valve or other key parts are found to be damaged, they should be replaced in time.
Q: How to adjust the output pressure of the air pressure reducing valve?
A: The output pressure of the air pressure reducing valve can be adjusted by adjusting the bolt. The adjusting bolt is located on the valve core. By rotating the adjusting bolt, the strength of the spring can be changed, thereby changing the opening position of the valve core and thus changing the output pressure.
Q: How to adjust the flow rate of the air pressure reducing valve?
A: The flow rate of the air pressure reducing valve can be adjusted by changing the opening position of the valve. The opening position of the valve can be changed by adjusting the valve stem.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting an air pressure reducing valve?
A: The following factors should be considered when selecting an air pressure reducing valve:
Air source pressure: The input pressure of the air pressure reducing valve should be less than the air source pressure.
- Output pressure: The output pressure of the air pressure reducing valve should meet the system requirements.
- Flow: The flow of the air pressure reducing valve should meet the system requirements.
- Ambient temperature: The air pressure reducing valve should be able to adapt to the ambient temperature of the system.
Q: What matters should be paid attention to when maintaining the air pressure reducing valve?
A: The following matters should be paid attention to when maintaining the air pressure reducing valve:
- Regularly check whether the air pressure reducing valve is firmly connected and damaged.
- Check the air pressure reducing valve seal regularly for damage.
- Periodically check the spring of the air pressure reducing valve for damage.
- Clean the internal parts of the air pressure reducing valve regularly.
Q: How to extend the service life of the air pressure reducing valve?
A: The service life of the air pressure reducing valve can be extended by the following methods:
- Correct selection: Choose an air pressure reducing valve that suits your system requirements.
- Correct installation: Install the air pressure reducing valve according to the correct method.
- Proper use: Use the air pressure reducing valve in the correct way.
- Regular maintenance: Maintain the air pressure reducing valve regularly to detect and eliminate faults in a timely manner.