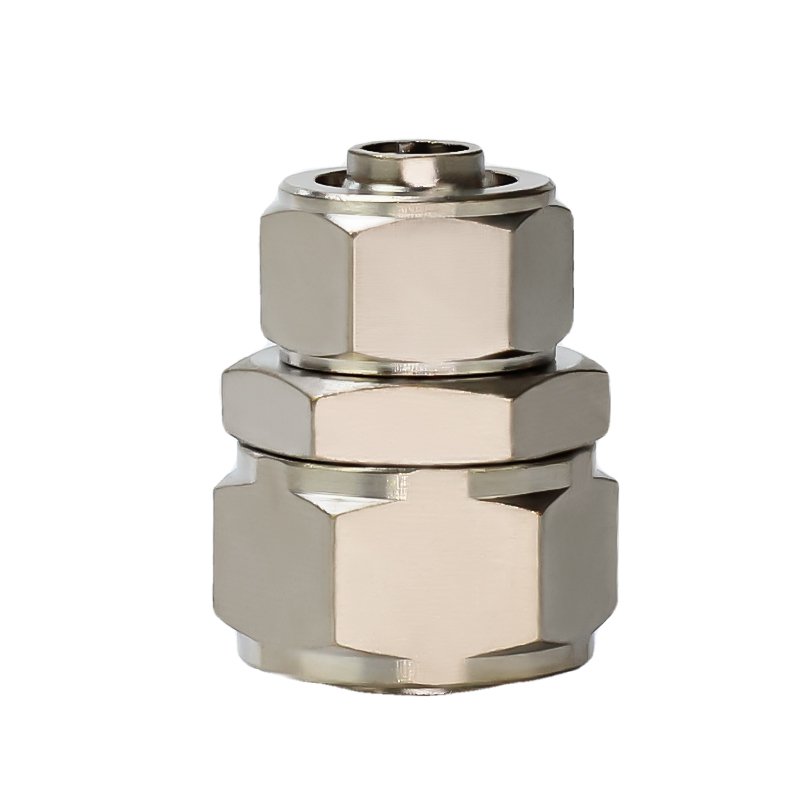
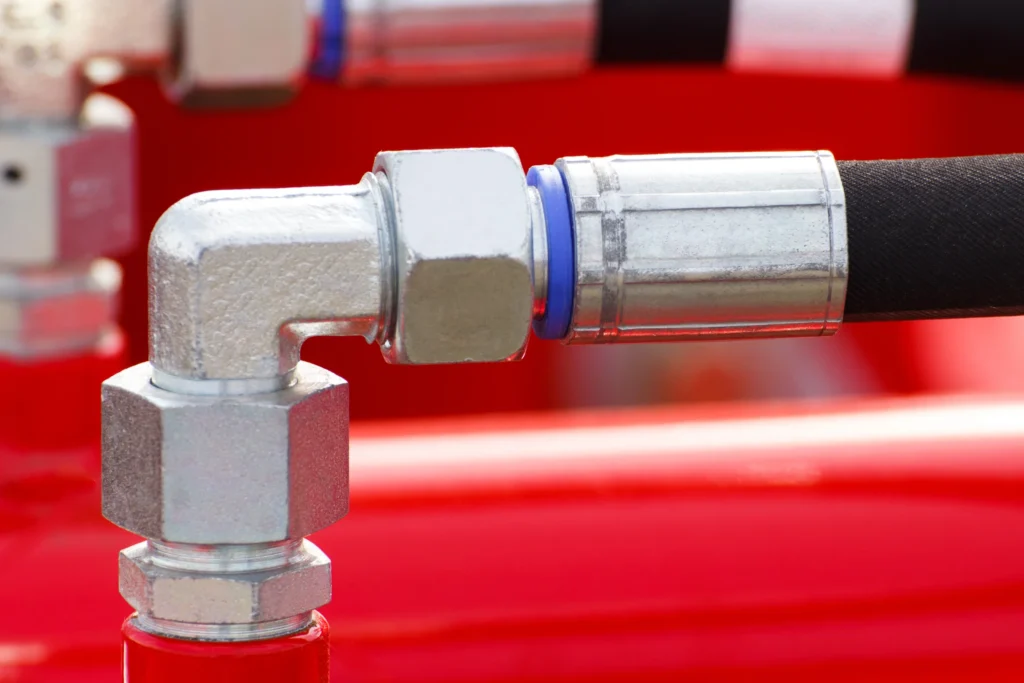
What is a copper barb connector?
Copper barb connector is a pipe fitting widely used in fluid delivery systems, mainly used for quick connection and disconnection of hoses and hard pipes. This kind of connector is usually threaded on one end and designed with a barb-shaped protrusion on the other end, which is used to insert the hose and form a tight joint to prevent the pipe from falling off or leaking. Copper, as a material for connectors, is widely used because of its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. It is especially suitable for applications that require corrosion resistance and hygienic environments, such as drinking water systems, medical equipment, and certain chemical processing systems. Designed with durability and economy in mind, copper barb connectors provide a reliable and efficient solution to meet modern industry demands for fluid delivery system stability and safety.

Functions and characteristics of copper barb connectors
The main function of copper barb connectors is to achieve a stable connection between hoses and hard pipes or equipment. Due to the properties of copper, these connectors play an integral role in many systems. Here are some of the key functions and features of copper barb connectors:
- Quick connection and disassembly: Copper barb connectors make pipe installation and maintenance faster and more convenient, and are suitable for systems that require frequent replacement or maintenance.
- Good sealing: The barb design ensures a tight fit between the hose and the connector, effectively preventing leakage of liquid or gas.
- Corrosion resistance: Copper has excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for a variety of environments, such as acidic or alkaline occasions.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Copper’s good thermal and electrical conductivity makes it useful in specific thermal management and electrical conductivity applications.
- Durability: The stability and durability of the copper material ensures long-term connector life, maintaining performance even under extreme temperatures and pressures.
- Strong adaptability: Different specifications and models of copper barb connectors can meet the needs of hose connection of various diameters and lengths.
- Environmentally friendly: Copper is a recyclable material, and the use of copper barb connectors meets the requirements of sustainable development and environmental protection.
- Aesthetics: The color of the copper material itself adds a certain degree of aesthetics to the equipment, especially when used in visible parts, it improves the appearance and texture of the overall equipment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Copper Barb Connectors
The advantages and disadvantages of copper barb connectors reflect their performance in real-world applications:
Advantage:
- Corrosion resistance: Copper has excellent corrosion resistance and can resist the attack of many chemicals, especially in water treatment and marine environments.
- Good electrical and thermal conductivity: This makes copper barb connectors suitable for systems that need to conduct heat or current.
- High mechanical strength: Copper material has sufficient strength and hardness, can withstand a certain amount of pressure and impact, and ensures stable connection.
- Easy installation: The simple design of the barb structure makes installation and maintenance easy and fast, without the need for special tools.
- Wide range of applications: Can be used in a variety of industrial applications, such as water treatment, gas transportation, cooling systems, etc.
- Aesthetics: Copper material has natural luster and color, which can improve the overall aesthetics of the device.
Shortcoming:
- Cost Issues: Copper generally costs more than other materials such as plastic or steel.
- Heavier weight: Copper is heavier than many other metals and may not be suitable for applications where weight is critical.
- Poor flexibility: Compared with connectors made of soft materials, copper barb connectors are slightly less flexible and may not be suitable for pipelines that require flexible bending.
- Limited by the chemical compatibility of copper: Although copper has excellent corrosion resistance, corrosion can still occur in certain chemical environments.
- Thermal expansion problem: Copper has a large thermal expansion coefficient, and temperature changes may affect the sealing performance of the connection.
- Theft Problem: Due to its high recycling value, copper products are sometimes targeted for theft.
Main components of barb connector
Barb connectors are usually simple in structure, but every part is crucial. The main components include:
- Barb part: It is the core of the connector. A series of barb-shaped protrusions extend along one end of the connector to grip the inner wall of the hose to ensure that the pipe does not fall off.
- Connecting threaded part: Usually located at the other end of the barb connector, it can be internally or externally threaded and is used to secure the connector to the corresponding pipe or equipment.
- Seals: Some barb connector designs include one or more seals, usually located near the threaded portion, to provide additional sealing to prevent leakage of liquids or gases.
- Grip Sleeve (if applicable): Some designs have a sleeve that fits over the outside of the hose to provide additional strength at the connection.
- Clamping devices (if applicable): To increase the strength of the connection, a clamping device such as a clamp or clamp may be used to further secure the engagement between the hose and the barb connector.
- Transition body: Between the barb and the thread, there may be a transition body, which helps to strengthen the structure and also serves as a support surface for clamping the hose.
- Tail: In some specific designs, the tail may have a tab or other mechanism to allow the user to attach or detach more easily.

Barb connector styles and the design principles behind them
Barb connectors come in a variety of styles and are designed with a few basic principles in mind to ensure their functionality and reliability.
Style:
- Straight-through barb connector: The most common type, used when connecting hoses on both ends.
- Conversion barb connector: One end is a barb, and the other end may be a thread or other type of interface, used to connect different types of pipes.
- Tee or Four-Way Barb Connector: Has multiple outlets and is used to distribute fluid from one main line to multiple branch lines.
- Elbow barb connector: An elbow designed with a certain angle based on the barb, used at the corners of pipes.
- Reduced diameter barb connector: Barbs of different diameters are designed to connect hoses of different diameters.
- Valved Barb Connector: Designed with an integrated valve to control the flow of fluids.
Design principle:
- Reliability Principle: Barb connectors must be securely attached to the hose to prevent them from falling off under pressure.
- Sealing principle: Connector design ensures that leakage does not occur at the connection point, usually through the tight fit of barbs and possible sealing rings.
- Durability Principle: Materials are selected and structures are designed to resist environmental factors such as corrosion, oxidation and mechanical wear.
- Principle of simplicity: Ease of installation and removal is an important consideration in the design of barb connectors, which usually do not require additional tools.
- Adaptability principle: The design must be able to adapt to different sizes and types of hoses, including hoses that are resistant to high temperatures and chemical corrosion.
- Economic rationale: Despite the use of high-quality materials, the design also takes into account cost-efficiency, ensuring that it is as economical as possible without sacrificing performance.
What are the commonly used materials for barb connectors?
Barb connectors can be made from a variety of materials, each with its own specific properties and applicable scenarios. Here are some commonly used materials:
- Copper: Copper is a common material for manufacturing barb connectors due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good electrical conductivity. It is particularly suitable for applications requiring hygiene, such as drinking water systems.
- Stainless Steel: Offers extremely high resistance to corrosion and heat, making it suitable for harsh industrial environments, including handling corrosive liquids and high-temperature applications.
- Plastics (e.g., polyethylene, polypropylene): Provide good chemical stability and lower cost, often used in low-pressure applications. Plastic barb connectors are lightweight and unbreakable, making them suitable for a variety of commercial and home applications.
- Brass: Brass barb connectors are widely used due to their good mechanical properties and moderate price. Brass’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for a variety of environments, especially where highly corrosive chemicals are not involved.
- Aluminum: Due to their lightweight and corrosion resistance, aluminum barb connectors are suitable for applications that require lightweight or have certain thermal performance requirements.
- Nylon and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): These synthetic materials offer excellent chemical stability and flexibility. Nylon and PTFE are particularly suitable for applications requiring a high degree of chemical inertness.
Installation methods and steps for copper barb connectors
The process of installing copper barb connectors is relatively simple, but the correct steps and precautions can ensure a safe and reliable connection. Here are the installation methods and steps for copper barb connectors:
1. Prepare tools and materials:
- copper barb connector
- Corresponding diameter hose
- Plumbing scissors or saw (for cutting hose)
- Clamp (if required)
- Screwdriver or clamp tool (for tightening the clamp)
2. Measure and cut the hose: Determine the length of hose you need and use plumbing scissors or a saw to cut it accurately. Make sure the cuts are flat to avoid air or water leaks during installation.
3. Check the barb connector and hose: Check the barb connector for damage or defects and make sure the inner and outer surfaces of the hose are clean and free of foreign matter.
4. Connect the hose: Push one end of the hose evenly onto the barb part of the barb connector until the bottom of the hose touches the base of the connector. Make sure the hose covers all barbs evenly to provide the best seal.
5. Fix the hose:
- If using a clamp, place the clamp over the hose and slide it to where the hose meets the connector.
- Use a screwdriver or special clamp tool to tighten the clamp. Make sure the clamp applies even force to prevent the hose from slipping under pressure.
6. Check and test the connection:
- Before starting the system, carefully check every connection point to make sure there are no loose connections or air leaks.
- After starting the system, check for leaks. If a leak is detected, shut down the system immediately and readjust the connections.
7. Maintenance inspections: Regularly check the condition of connectors and hoses, especially in high-pressure or dynamic applications. Replace any worn or damaged parts to ensure long-term stable operation of your system.

Routine maintenance and troubleshooting
For routine maintenance and troubleshooting of copper barb connectors, reasonable care can significantly extend their service life and ensure system operation efficiency. Here are some key maintenance and troubleshooting steps:
Routine maintenance
Periodic inspection:
- Regularly inspect copper barb connectors and the hoses they connect to for wear, cracks, or corrosion.
- Check all clamps and other securing devices for looseness. In high pressure or vibration environments, fixtures may gradually loosen.
Cleaning and maintenance:
- Clean copper barb connectors regularly to remove dirt and chemical residue and prevent corrosion.
- Use an appropriate cleaner to clean copper materials and avoid using cleaners that may cause corrosion of the copper.
lubricating:
- If the connector assembly contains moving parts (such as valved models), lubricate it regularly to ensure smooth operation.
- Use a non-corrosive lubricant suitable for copper.
Replace damaged parts:
- Replace worn or damaged connectors and hoses promptly to prevent leaks and sudden failures.
Troubleshooting
Leak issues:
- If leakage is found at the connection, first check whether the clamp is loose. Readjust or replace the clamp.
- Check that the hose is installed correctly and is not damaged. If damaged, the hose needs to be replaced.
Blockage problem:
- If fluid flow is blocked, check to see if there is any foreign material blocking the inside of the copper barb connector.
- Clear the clog and check if the filters in the system need cleaning or replacement.
Corrosion issues:
- Periodically inspect copper barb connectors for signs of corrosion, especially if they are used in a chemically strong environment.
- If corrosion is found, evaluate whether the connector needs to be replaced with a material more suitable for the environment.
Difficulty operating:
- If a valved connector is difficult to operate, check to see if the valve needs lubrication or adjustment.
- Ensure free movement of all moving parts without obstruction.
By implementing these maintenance and troubleshooting measures, you can maximize the performance and reliability of your copper barb connectors, ensuring long-term stable operation of your system. Maintenance work can not only prevent sudden failures, but also detect potential risks in the early stages of problems, thereby avoiding greater losses.